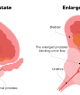
It rests below your bladder and in front of your rectum. It surrounds part of the urethra, the tube in your penis that carries pee from your bladder.
The prostate helps make some of the fluid in semen, which carries sperm from your testicles when you ejaculate.
This gland can grow
As you age, your prostate can become larger. It's a normal part of aging for most men.
By the time you reach age 40, your prostate might have gone from the size of a walnut to the size of an apricot. By the time you reach 60, it might be the size of a lemon.
Because it surrounds part of the urethra, the enlarged prostate can squeeze that tube. This causes problems when you try to pee. Typically, you won't see these problems until you're 50 or older, but they can start earlier.
Who might get an enlarged prostate?
BPH is common and cannot be prevented.
Age and a family history of BPH are two things that increase the chances you might get it.
1. about 8 out of every 10 men eventually develop an enlarged prostate;
2. about 90% of men over the age of 85 will have BPH;
3. about 30% of men will find their symptoms bothersome.
Symptoms
If you have trouble starting to urinate or have to go a lot, especially at night, these could be signals that you have an enlarged prostate.
Other signs and symptoms include:
1. Your bladder doesn't empty completely after you pee.
2. You feel the need to go out of the blue with no sensation of build up.
3. You may stop and start several times.
4. You have to strain to get any flow going.
Prostatitis is a swelling, inflammation or infection of the prostate gland. It can cause burning or painful urination, the urgent need to urinate, difficult or painful ejaculation, or pain in the area between the scrotum and rectum or in the lower back. It can occur to men at any age and should not be confused with cancer.
There are four types of prostatitis:
1. acute bacterial prostatitis;
2. asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis;
3. chronic bacterial prostatitis;
4. chronic prostatitis.
Prostate Cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer in men about 1 in 7 will be diagnosed during his lifetime and is the second leading cause of cancer death in men.
It is also one of the most treatable cancers, which is why it is crucial to seek annual screening and early diagnosis.